Public Trusts & Charitable Institutions – An Overview
May 9, 2021
“Trust is an obligation annexed to the ownership of property and arising out of a confidence reposed in and accepted by him for the benefit of another” – Indian Trusts Act
A public trust or charitable institution should have a defined object (For eg. Relief for poor, education, medical relief, etc.) which benefits a sufficiently larger section of public as distinguished from specific individuals.
A. How to incorporate a trust
Trust deed
Legal existence to the trust. Should be an irrevocable trust.
Settlor
Capable of creating a trust and dedicating his property to the trust.
Object
Purpose of the trust should be valid either religious or for a charitable purpose as the law prescribes.
Trustees
Manage the trust (can be a NRI as well)
B. Registration & Regulation
A public trust or a charitable institution shall register itself under the required legislations to get various benefits and recognitions. Following are the legislation and authorities which regulate trusts:
Societies
Act – Registrar of Societies
A trust registered under this Act should file the required documents with the office of the registrar at specified regular intervals.
Charities
Commissioner / State Acts
The offices of the Charities, Commissioners and their equivalent in various states are responsible for the general administration and supervision of public charitable trusts.
Income Tax Act – Directorate of Income Tax
Mandatory for every trust if it wishes to claim exemption from taxation under the provisions of the Income Tax Act, 1961.
Companies
Act – Registrar of Companies
If the trust is incorporated under Section 8 of the Companies Act, 2013, then registration and compliances under this Act becomes mandatory.
Central
Govt. – Ministry of Home Affairs
The Central Govt. would regulate and get involved in the cases where contribution is received from foreign sources. (Foreign Contribution (regulation) Act, 2010)
C. Income Tax:
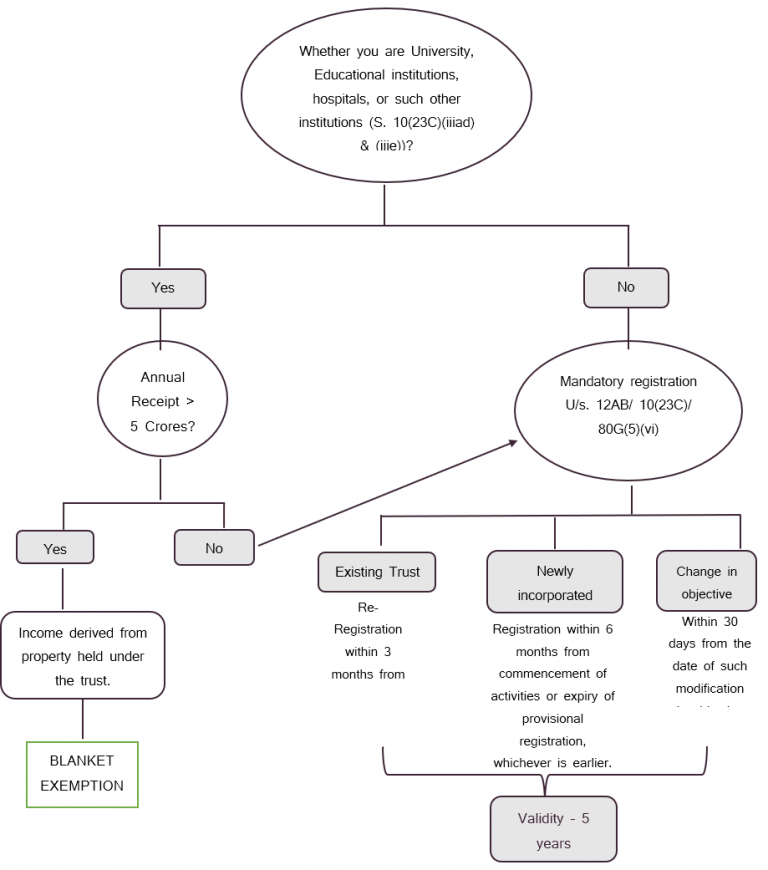
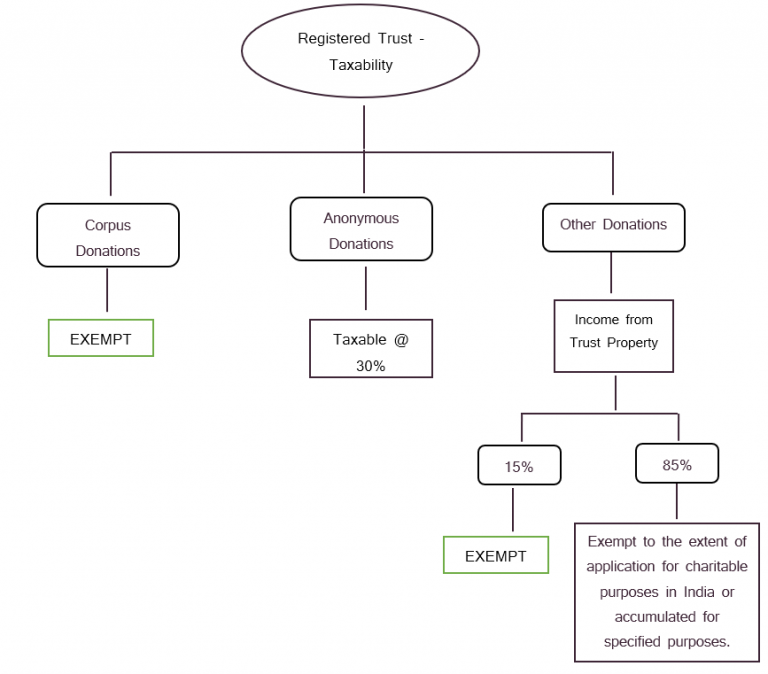
Filing of various returns & forms:
2. Form 9A – Accumulation of amount for 1 year
3. Form 10 – Accumulation of amount for 5 years
4. Form 10B – Audit Report
5. ITR 7 – Income tax return
D. Goods & Service Tax:
There are certain criteria for a charitable trust or an NGO to be exempted from GST. Exemption is given to the charitable & religious trusts, only if the following conditions are satisfied:
(a) Entities must be registered under Section 12AA of the Income tax Act, and
(b) Such services or activities by the entity are by way of charitable activities.
Charitable activity has been defined in Notification No. 12/2017-Central Tax (Rates) and a brief of the definition is depicted below:
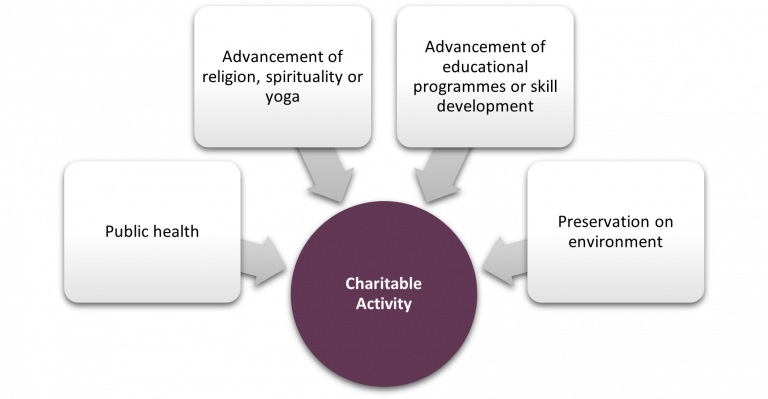
If any charitable trust or an NGO does not meet at least two of the criteria, then GST will be applicable, and the entity must register under GST.
Difference between the meaning of Charitable Activities as specified in GST Act & Income Tax Act:
Extract Section 2(15) of Income Tax Act 1961,
“charitable purpose” includes relief of the poor, education, yoga, medical relief, preservation of environment (including watersheds, forests and wildlife) and preservation of monuments or places or objects of artistic or historic interest, and the advancement of any other object of general public utility.
The major difference is the inclusion of the term “the advancement of any other object of general public utility”, in the definition of Charitable activity, which results in inclusion of various activities which may fall within this meaning i.e. advancement of any other object of general public utility. However, GST Act does recognize all such other activities as Charitable activity, only activities which are specified in the notification are considered as Charitable Activity and are exempt from GST.
Supply of goods by charitable trusts:
Goods Supplied by Charitable Trusts are taxable under GST unless the goods are specifically exempt under any notification by the government.
Other exemptions available for charitable & religious trusts registered under section 12AA of the Income Tax Act:
§ Services by way of
o Conduct of any religious ceremony
o Renting of precincts of a religious place meant for general public with conditions prescribed
§ Services by way of training or coaching in recreational activities relating to
o Arts or culture, or
o Sports
§ Services provided by Educational Institutions to its students, faculty or staff
§ Services received by Educational Institutions as mentioned below are exempt
o transportation of students, faculty and staff;
o catering, including any mid-day meals scheme sponsored by the Central Government, State Government or Union territory;
o security or cleaning or house-keeping services performed in such educational institution;
o services relating to admission to, or conduct of examination by, such institution.
If such educational institution gives property owned by such institution on rent to others, no exemption will be available for such services.
§ If trusts are arranging residential or non-residential yoga and meditation camps by receiving donation or other charges from the participants, these will not be considered charitable activities and it will definitely be covered under the GST.
§ Services by way of healthcare services by a clinical establishment, an authorized medical practitioner or para-medics.
(*healthcare services and clinical establishment as defined in the notification.)
§ Services by way of transportation of patients to and from a clinical establishment.
There are many other activities in which Charitable Trusts work, the taxability of those activities will be dealt on case-to-case basis. However, all the activities of Charitable & Religious Trusts are not exempted from taxability under GST.
Disclaimer:
The above is a very brief writeup and solely for educational & information purposes only. It does not constitute an advice or a legal opinion or personal views. There may be possibility of different view on the various subject matter discussed.